Shanghai Digi-United Biotechnolgoy Co., Ltd. is a high-tech company focusing on the development of optical imaging instruments and fluorescent probes as well as their biological application in the second near-infrared (NIR-II, 900-1700 nm) optical window. We have more than 30 people, 98% of whom have doctorate and master's degree, including a material synthesis team with interdisciplinary in chemistry, materials science, biology, medicine and other fields, and a complete technical team in electromechanical, optical and software systems for mechanical design and production.
Our main products include NIR-II in vivo fluorescence imaging system, Vis/NIR-II in vivo fluorescence imaging system, NIR-II microscope system and compact NIR-II fluorescence imaging system for in vivo small animal imaging. We have also developed a unique NIR-II fluorescence lifetime imaging system, which can be applied to quantitatively imaging and sensing in deep tissue. Benefiting from less tissue absorption, tissue scattering as well as tissue autofluorescence background noise, optical imaging in the NIR-II window has a deeper tissue penetration depth with higher imaging resolution and signal-to-noise ratios, as compared to conventional imaging in the visible region. In addition to the fluorescent optical imaging systems, we also provide NIR-II fluorescent probes with user-desired modification, including organic small molecules and inorganic nanoparticles (lanthanide based nanoparticle and quantum dots). These probes can be used for real-time imaging in cells, biological tissues and small living animals for different biological models with high signal-to-noise ratios, and also can be designed to perform biological sensing. Based on our advantages on instrument and fluorescent probes, we undertake scientific research and experimental service projects, including the development of tumor, cardiovascular, inflammation, digestive system, implantable equipment, lung function, bone related diseases, urology, gynecology, skin diseases and other related models for NIR-II imaging studies.
Our end-users include many famous universities, scientific research institutions and hospitals in China, the United States and Europe. Our technology and products provide strong support for its scientific research projects and medical experimental research.


About imaging in the second near-infrared window (900-1700 nm)
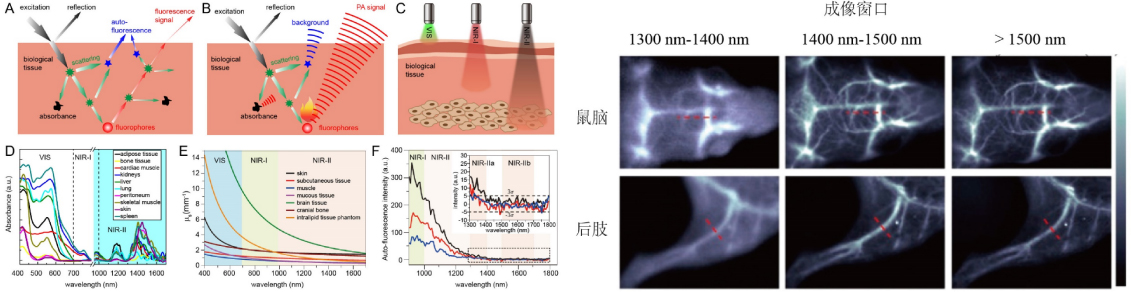
Conventional fluorescence imaging was mainly performed in the visible and the first near-infrared region (400 nm~900 nm), and was widely used in microscopic fluorescence imaging. However, up to now, there have been obvious drawbacks in the wide-field fluorescence imaging using light this region:
1. Biological tissue shows a high scattering in this region, which induces much lower resolutions of the images in deep tissue as compared to microscopic fluorescence imaging.
2. Tissue autofluorescence background signal is strong in this region, which causes the deep-tissue imaging with low signal-to-noise ratio.
3. The high absorption of tissue in this region reduces the penetration depth for wide-field imaging.
Light in the NIR-II window has low tissue scattering coefficients and absorption, and causes almost zero-tissue autofluorescence background noise. Therefore, optical imaging in the NIR-II window can realize high tissue penetration depth (> 1 cm) and high spatial resolution (< 20 um).